Localization
The goal of the localization process is to consistently produce high quality translations release after release through collaboration between the international community, translators, project managers, language leads, and the core team.
Interested in contributing to product translations?
If you're interested in contributing translations to Mattermost, learn more about getting started with Mattermost translations by visiting the translation contribution documentation.
Join us on the Mattermost Community server
We strongly encourage all translators to join us in the Mattermost localization channel on the Mattermost Community server.
In the localization channel, you can:
Discuss translation questions, concerns, and best practices with both Mattermost staff and the Mattermost translation community.
Learn more about string context, including audience and product area.
Review important translation timelines, deadlines, announcements, and notifications.
Escalate any challenges you're experiencing as a product translator.
Tip: We also encourage language experts to create language-specific localization channels on the Mattermost Community Server. See examples of current channels including Italian, German, and Swedish.
Active translation projects
You can contribute to the following active translation projects:
Translation project
Translation server URL
Channels
https://translate.mattermost.com/projects/mattermost/
Playbooks
https://translate.mattermost.com/projects/playbooks/
Desktop app
https://translate.mattermost.com/projects/mattermost/mattermost-desktop/
Mobile app
https://translate.mattermost.com/projects/mattermost/mattermost-mobile-v2/
Calls
https://translate.mattermost.com/projects/calls/
The general localization process is described in the following sections on this page.
Translate English product strings into additional languages
Mattermost is developed in US English, and officially supports 20 additional languages. Getting started is easy.
Join the Mattermost translation server
Important note: While it's common to contribute to Mattermost in GitHub, product translations is a notable exception. You must contribute to Mattermost translations on the Mattermost translation server. Please don't attempt to submit translations in GitHub via pull requests (PRs) as your translations will be overwritten with the next PR update.
Confirm whether the language you want to translate is one we officially support or is a work-in-progress (WIP) language. To contribute to the supported languages you need extra permissions, this is a safety measure.
Requesting these permissions can be done in the Mattermost localization channel or with a direct message to John Combs or Tom De Moor.
Only supported languages are available in-product by selecting Settings > Display > Language. Any language that isn't officially supported is considered a work-in-progress language. Work-in-progress languages become officially supported languages when the following two conditions are met:
The (WIP) language reaches or exceeds the Beta translation quality threshold across three consecutive releases; and,
A language expert is available for at least six months of maintenance updates.
See the section on translation quality for further details.
Tip: We encourage translators to help us support additional languages and regional variants.
Review translation rules written by localization leads, when applicable
Translation rules and glossaries are available for the following languages:
Tip: We welcome rules and guidelines for all supported languages. If these translation assets don't exist for the language you're interested in, perhaps you'd be open to help create them?
Omit error strings from localization process
When an error string isn’t visible to end users, engineering teams must use model.NoTranslation as the error id to implement a model.AppError without a translation. See examples of this approach in the mattermost/mattermost-server repository on GitHub.
Error strings that use model.NoTranslation as the error id are omitted from Mattermost translation workflows, and aren't surfaced up in Weblate to translators.
Product localization process
The following flow diagram outlines the product localization flow from the translation server to the Mattermost codebase:

New and updated US English source strings are automatically added to the translation server each time a GitHub PR containing string changes is merged by Mattermost Engineering.
The translation server pulls the latest string changes as they are committed to the codebase.
Translators are notified when strings are new or changed.
Translators add and update string translations.
Each Monday, at 22:00 GMT, a job opens PRs in GitHub to the main branches of the mattermost-server and mattermost-webapp, mattermost-mobile, and mattermost-desktop repositories. Weekly PRs contain several commits, one per modified language. Changes are merged back into each branch after a security/consistency review.
PRs will also be submitted on the day of major feature complete, code complete, and release candidates to ensure latest translations are included in the release.
Translation PR review process
Translation PRs are created automatically on Mondays. These PRs are also posted to the i18n PRs channel. Engineering PR reviews focus on ensuring that unexpected characters aren't injected into strings. If security concerns are found, Engineering notifies the Security team.
The translation PRs should be reviewed and merged as soon as possible to avoid blocking translators.
Important Note: Engineering teams must merge these PRs into the codebase using "merge commit" (technically also known as "rebase and merge"), and /never/ "squash and commit". The latter breaks the automated translation server flow, locks the translations, and forces manual fixes.
Translation quality
In order for users to understand the accuracy and coverage of language translations, quality levels are explicitly defined for each language as one of: Official, Beta, or Alpha.
Official
100% of translation verified by someone deeply knowledgeable in Mattermost functionality.
100% of translation verified by someone deeply knowledgeable in target language.
No translation may be out-of-date due to changes to English-language text since the last translation and review cycle.
Language must have at least one official reviewer who maintains the language with updated strings imported to the Translation Server over time.
Language must have been in use for at least three full release cycles where end users in target language can share feedback and corrections.
Official languages are listed in Account Settings > Display > Language.
Beta
At least 90% of string translation verified by someone deeply knowledgeable in Mattermost functionality and in the target language. Languages at risk for ongoing maintenance can require a higher translation threshold closer to 100%.
Up to 10% of translation may be out-of-date due to changes to English-language text since the last translation and review cycle.
Beta languages are listed in Account Settings > Display > Language appended with (Beta).
Alpha
Translation has not yet reached Beta quality. An official language may be changed back to Beta or Alpha if the specified requirements are not met for a release. Similarly, Beta languages may be dropped back to Alpha.
Alpha languages are listed in Account Settings > Display > Language appended with (Alpha).
Message syntax
react-intl is used to format localized messages in React packages of mattermost. This library uses the ICU MessageFormat syntax, which is a Unicode standard used in many programming languages.
ICU Message syntax guide is a good resource to familiarize yourself with. What's most important here is to read the sections dedicated to Quoting/Escaping, and how placeholders are managed, including placeholder arguments such as plural, select, number, and so on.
The Mattermost translation server will automatically check and validate translations in the editor. If there are any failing checks, you will want to review them to spot any potential typos or errors. These checks can be quite helpful in spotting subtle issues in long or more complex translation strings.
Additionally, Online ICU Message Editor is a good resource that supports live-editing. It's great for previewing how a string will appear in context, don't hesitate to use it.
Resources for translating technical terms
Some terms used in Mattermost may be technical. If you don't know how to translate a specific term:
Where applicable, review how the term has been translated in other locations of the translation you are contributing to.
Where applicable, review machine translation suggestions provided via the Deep-L integration.
Use a translation engine to learn how others have translated the term.
Use the Microsoft open linguistic portal.
Ask your question in the Mattermost localization channel.
Test translations
A Mattermost Cloud workspace is available for all Mattermost translators to understand string context, including the target user and the task the user is performing when they encounter the string. This workspace is updated weekly; however, translations can lag behind Cloud releases by up to two weeks.
Missed translations
If you encounter a product string that hasn't yet been translated in the Mattermost Cloud workspace, the string is either not yet translated, or the workspace hasn't been updated yet to include that translated string.
You can search for strings in the English localization resource file within a respective GitHub repository to confirm whether a missed translation or an outdated workspace. The following resource files are available for US English strings:
Each Mattermost GitHub repository above will contain additional resource files for each supported language. If a string appears in the en.json file, but displays in English in a localized resource file, that string likely isn't translated yet. An English string in the en.json file that is translated in its associated localized resource file likely indicates that the workspace hasn't been updated yet to include that translation.
If you discover a missing translation, please let us know in the Mattermost localization channel.
Translation maintenance
Product translations require updates on a monthly basis as features are added and changed. Weekly updates and deadlines are announced in the Mattermost localization channel.
Below are current official reviewers and maintainers for officially supported languages. Official reviewers submit final translations for languages; maintainers suggest translations and step in when official reviewers aren't able to help in a certain release.
If you're interested in contributing to the process, please join the Mattermost localization channel to discuss.
Bulgarian
TBD (Open role)
TBD (Open role)
Español - Spanish
TBD (Open role)
TBD (Open role)
Français - French
TBD (Open role)
TBD (Open role)
Magyar - Hungarian
TBD (Open role)
TBD (Open role)
Italiano - Italian
TBD (Open role)
TBD (Open role)
Português do Brasil - Portuguese
TBD (Open role)
TBD (Open role)
Română - Romanian
TBD (Open Role)
TBD (Open role)
Yкраїнська - Ukrainian
TBD (Open role)
TBD (Open role)
中文 (繁體) - Traditional Chinese
TBD (Open role)
TBD (Open role)
Displaying Work In Progress languages
Systen Administrators can enable Work In Progress languages in the System Console -> Localization -> Enable Experimental Locales. We labeled in Weblate the most common used strings for users with "First User Experience". These strings are a good starter for new translations.
Administrative tasks
Translation server admins must grant all new translators specific Weblate permissions before translators can start contributing to official supported languages. Translation server admins can reach the server's administration tools by going to https://translate.mattermost.com/admin/.
Note: Admin tools on the translation server are being updated to make roles and permissions maintenance easier. If you require translation permissions, please let us know in the Mattermost localization channel.
To add a new WIP language:
Select a component on the resulting page, then select Tools > Start new translation.
Select the languages you want to add, then Start new translation.
Translators permissions scheme
The goal of the permissions scheme is to be as open as possible to new contributors while keeping the product as safe as possible. Therefore, everyone who joins our translation server is able to make translations for the WIP languages, and add suggestions to the shipped languages. Our shipped language translators can translate their language, add make suggestions to other shipped languages, and add translations to WIP languages.
The following Weblate roles control access:
Mattermost@DefaultUserTranslateWIP: Everyone who joins the Weblate translation server is automatically added to this group, and can translate WIP languages.
Mattermost@DefaultUserSuggestionsToShipped: Everyone who joins the server is automatically added to this group, and can make suggestions to the shipped languages.
mattermost@Translators [language]: A group for each shipped language. Add translators for each language here.
Setting up new translations on Weblate
Step 0 - Permissions
Register an account and request admin permissions to the Weblate server from Carrie Warner or Tom De Moor.
Step 1 - Create a new Project (optional)
This step makes sense when the project has its own repository (e.g. Calls) or if it's helpful to have a separate translation entry point. Another option is to simply skip this step, and add a new component to an existing project.
Note: Make sure to enable reviews for the project. In Weblate, go to Project Settings, select the Workflow tab, and select Enable Reviews:
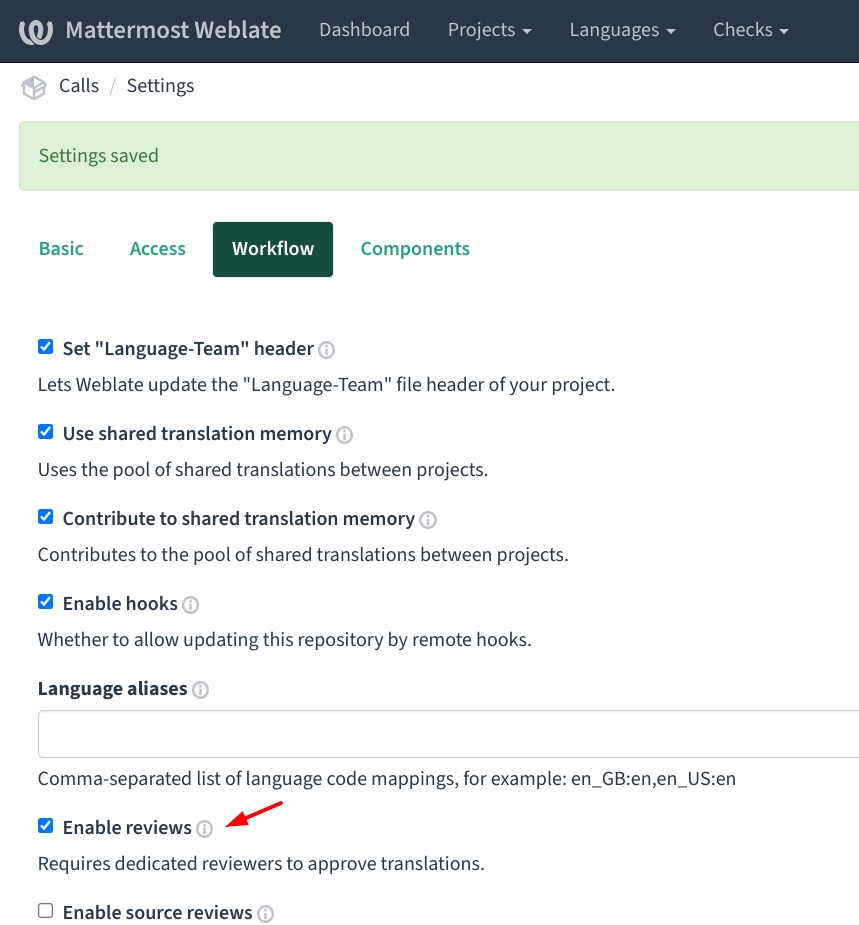
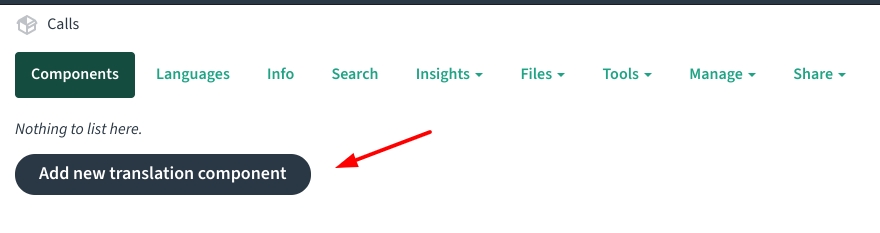
Step 2 - Add component(s)
Add a new component under the project.
Base configuration should look as follows:
Version control system should be set to Github pull request.
Source code repository should be set to the GitHub repository where the translation files are stored.
Repository branch should be set to the primary branch where translations should get merged into (usually either
masterormain).
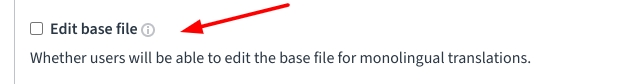
When you select Continue, Weblate will attempt to scan the repository to find any existing translation files paths. You can now select the one you'd like to cover with this component.
Uncheck Edit base file as it will prevent contributors from modifying the default language file and prevent potential conflicts.
Set Translation flags to ignore-inconsistent, ignore-same, icu-message-format.

Step 3 - Give translators access to your project
Access for the shipped languages is restricted to approved users. You must give access to your project on a per-language basis.

Step 4 - Repository hooks
Repository hooks (usually GitHub hooks) are needed to keep the translation files on Weblate in sync with the ones commited to the project repository.

You can create a ticket for the Release team to request enabling the hooks.
How to promote a WIP-language to shipped
You have to add the new language to the Mattermost platform and to Mobile For Playbooks and Calls no actions are needed
Step 1 - Adding the language to the Mattermost-platform
Add the language code to
server/public/shared/i18n/i18n.goAdd the language to
webapp/channels/src/i18n/i18n.jsxIn the
webappdirectory, runnpm run test:updatesnapshotAdd the modified
webapp/channels/src/components/admin_console/__snapshots__/schema_admin_settings.test.jsx.snapto your commit.Don't add string translations to the PR.
Here is an example PR you can use as a starting point.
Step 2 - Adding the language to Mobile
Add the language to
app/i18n/index.tsAdd the language to
app/i18n/languages.ts
Here is an example PR you can use as a starting point.
Step 3 - Adding the language to the Desktop-platform
Import the translation file into
i18n/i18n.ts, and add the language to the menu.
Here is an example PR you can use as a starting point.
Last updated
Was this helpful?